
What is Threaded Bushing?
304H Threaded Bushing are generally processed by cutting and forging a hexagonal rod, and uses a wide variety of thread types. It is an internal and external threaded fittings and used to combine two different diameter pipes. So has an irreplaceable place in the pipeline connection.

Hex Head Bushing

Flush Bushing
Flush Bushing is the type without head and Hex Head Bushing is the general type. They are ASME B16.11 Threaded Fittings and available in stainless steel, carbon steel and alloy steel.
Hex Head Bushing Dimensions

Hex Head Bushing Dimensions
Normally they are not identified by class. They may be used for ratings up to class 6000.
| Standard | ASME B16.11 |
|---|---|
| Technique | Forged |
| Thread type | FNPT, MNPT, BSPP, BSPT |
| Diameter | 1/8-4 inch |
| Stainless Steel Bushing | ASTM A182 F304/304L/304H, F316/316L/316H, F310/310H |
| Carbon Steel Bushing | ASTM A105, A694 F42, F52, F60 |
| Alloy Steel Bushing | ASTM A182 F1, F5, F11, F22, F91 |
Hex Head Bushing Weight in kg
| NPS | Approximate Weight (kg) |
|---|---|
| 1/8 | 0.01 |
| 1/4 | 0.03 |
| 3/8 | 0.05 |
| 1/2 | 0.08 |
| 3/4 | 0.16 |
| 1 | 0.35 |
| 1 1/4 | 0.56 |
| 1 1/2 | 0.65 |
| 2 | 1.26 |
| 2 1/2 | 2.38 |
| 3 | 3.5 |
| 4 | 8.31 |
Stainless Steel F304H Pipe Fittings
It is an austenitic chromium-nickel steel alloy and the greater carbon content delivers an increased tensile and yield strength. Both short term tensile strengths and long term creep strengths are higher for these high carbon grades.
They have good corrosion resistance to atmospheric and many organic and inorganic chemicals, and can be used in foods and beverages industries. The austenitic structure also gives these grades excellent toughness, even down to cryogenic temperatures.
Our SS 304H Threaded Bushing are used for a wide variety of home and commercial applications with excellent corrosion resistance, high ease of fabrication, outstanding formability, and tremendous strength.
A182 304H Threaded Bushing Chemical composition %
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 max | 2.0 max | 0.75 max | 0.045 max | 0.03 max | 18-20 | 8-10.5 |
A182 304H Threaded Bushing Mechanical Properties
| Density | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength (0.2% offset) |
Elongation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.0g/cm3 | 1400℃ | 515 Mpa | 205 Mpa | 35% |
304H Stainless Steel Equivalent Grades
| Werkstoff NR. | UNS |
|---|---|
| 1.4301 | S30409 |
SS316H Fittings

SS316H Fittings
It is versatile in application and can be the material of wrought Butt Weld Fittings and Forged Socket Weld Fittings and Threaded Fittings.
SS316H Pipe Fittings that our company can provide are Butt Weld 90 Degree Elbow, Socket Weld Full Coupling, Threaded Half Coupling, Butt Weld Eccentric Reducer, Threaded Nipple, Socket Weld Reducing Tee, Weldolet, Sockolet, Threadolet, Threaded Plug.
Usually Stainless Steel Fittings are used in Petrochemicals, Oil & Natural Gas Organization, Fats, Fertilizers, Sugar Mills & Distilleries, Cement Industries, Ship Builders, Paper Industries, Pumps, Automation, Paints, Steel Industries, etc.
Solution Treatment of 304H Threaded Bushing
It plays a vital role in the quality and safety of pipe fittings. It is necessary for stainless steel fittings to adopt solution treatment to enhance the safety.
Austenitic stainless steel is softened by heat treatment and heated to about 950-1150 degrees, and keep the temperature for a certain period of time, so that carbides and various alloying elements are uniformly dissolved in austenite.
The metal molecular structure, magnetic properties and physical properties have changed after Stainless Steel Fittings processing. It can restore the corrosion resistance that is affected after processing, and at the same time obtain the hardness required for the stainless steel, to ensure the performance of pipe fittings.
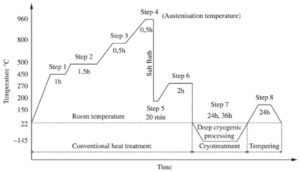
Solution Treatment of Stainless Steel
Three Element of Solution Treatment
They have a great influence on the corrosion resistance and appearance brightness of stainless steel, and play a decisive role in the processing properties of stainless steel.
1.Temperature
The temperature should reach 950-1150 degrees Celsius to have a softening effect, and the hardness can be reduced to less than 220 HV. If the temperature is not properly controlled, various quality defects are prone to occur.
2. Time
During the heating process, the residual ferrite content decreases as the heating time increases.
3. Heat Rate and Preservation
Since the stainless steel has a low thermal conductivity, so the heating process should be slow. If the heating rate is too fast, deformation is likely to occur.
The whole process takes about 40 minutes.
Latest News
 02 8 月 2019Copper Nickel Flanges UNS C70600Zizi offers ISO certified copper nickel flanges, stores large quantity of Cu-Ni 90/10 weld neck flan...
02 8 月 2019Copper Nickel Flanges UNS C70600Zizi offers ISO certified copper nickel flanges, stores large quantity of Cu-Ni 90/10 weld neck flan...  29 7 月 2019Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings ManufacturerZizi is stainless steel buttweld fittings manufacturer, we offer stainless steel pipe elbow, tee, ca...
29 7 月 2019Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings ManufacturerZizi is stainless steel buttweld fittings manufacturer, we offer stainless steel pipe elbow, tee, ca...  19 7 月 2019Steel Pipe Nipple Types, Dimensions and MaterialsBasic pattern of steel pipe nipple is a short piece of pipe with threads at both end or at one end....
19 7 月 2019Steel Pipe Nipple Types, Dimensions and MaterialsBasic pattern of steel pipe nipple is a short piece of pipe with threads at both end or at one end....
